“Everything we love about civilization is a product of intelligence, so amplifying our human intelligence with artificial intelligence has the potential of helping civilization flourish like never before – as long as we manage to keep the technology beneficial.“Max Tegmark, President of the Future of Life Institute
What is exactly AI in an easy way to understand its existence???
THE ANSWER?
Commonly AI or Artificial Intelligence is a machine or a computer program that learnt how to do tasks that required forms of INTELLIGENCES that are usually done by human. And to take it another way, intelligence comes in many different aspects. We have many type of AI's that are good in particular subsets of intelligence.
Below are the examples of mentioned ;
Starting from the creation of AI's like SIRI to self-driving cars, artificial intelligence (AI) is progressing rapidly. While science fiction often portrays AI as robots with human-like characteristics, AI can encompass anything from Google’s search algorithms to autonomous weapons.
Artificial intelligence today is properly known as narrow AI (or weak AI), in that it is designed to perform a narrow task (e.g. only facial recognition or only internet searches or only driving a car). However, the long-term goal of many researchers is to create general AI (AGI or strong AI). While narrow AI may outperform humans at whatever its specific task is, like playing chess or solving equations, AGI would outperform humans at nearly every cognitive task.
Artificial Intelligence History
The term artificial intelligence was coined in 1956, but AI has become more popular today thanks to increased data volumes, advanced algorithms, and improvements in computing power and storage.
Early AI research in the 1950s explored topics like problem solving and symbolic methods. In the 1960s, the US Department of Defense took interest in this type of work and began training computers to mimic basic human reasoning. For example, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) completed street mapping projects in the 1970s. And DARPA produced intelligent personal assistants in 2003, long before Siri, Alexa or Cortana were household names.
This early work paved the way for the automation and formal reasoning that we see in computers today, including decision support systems and smart search systems that can be designed to complement and augment human abilities.
While Hollywood movies and science fiction novels depict AI as human-like robots that take over the world, the current evolution of AI technologies isn’t that scary – or quite that smart. Instead, AI has evolved to provide many specific benefits in every industry. Keep reading for modern examples of artificial intelligence in health care, retail and more.
1950s–1970s : Neural Networks
Early work with neural networks stirs excitement for “thinking machines.”
1980s–2010s : Machine learning
Machine learning becomes popular.
Present Day : Deep Learning
Deep learning breakthroughs drive AI boom.
The Advantages for Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The Disadvantages for Artificial Intelligence (AI)
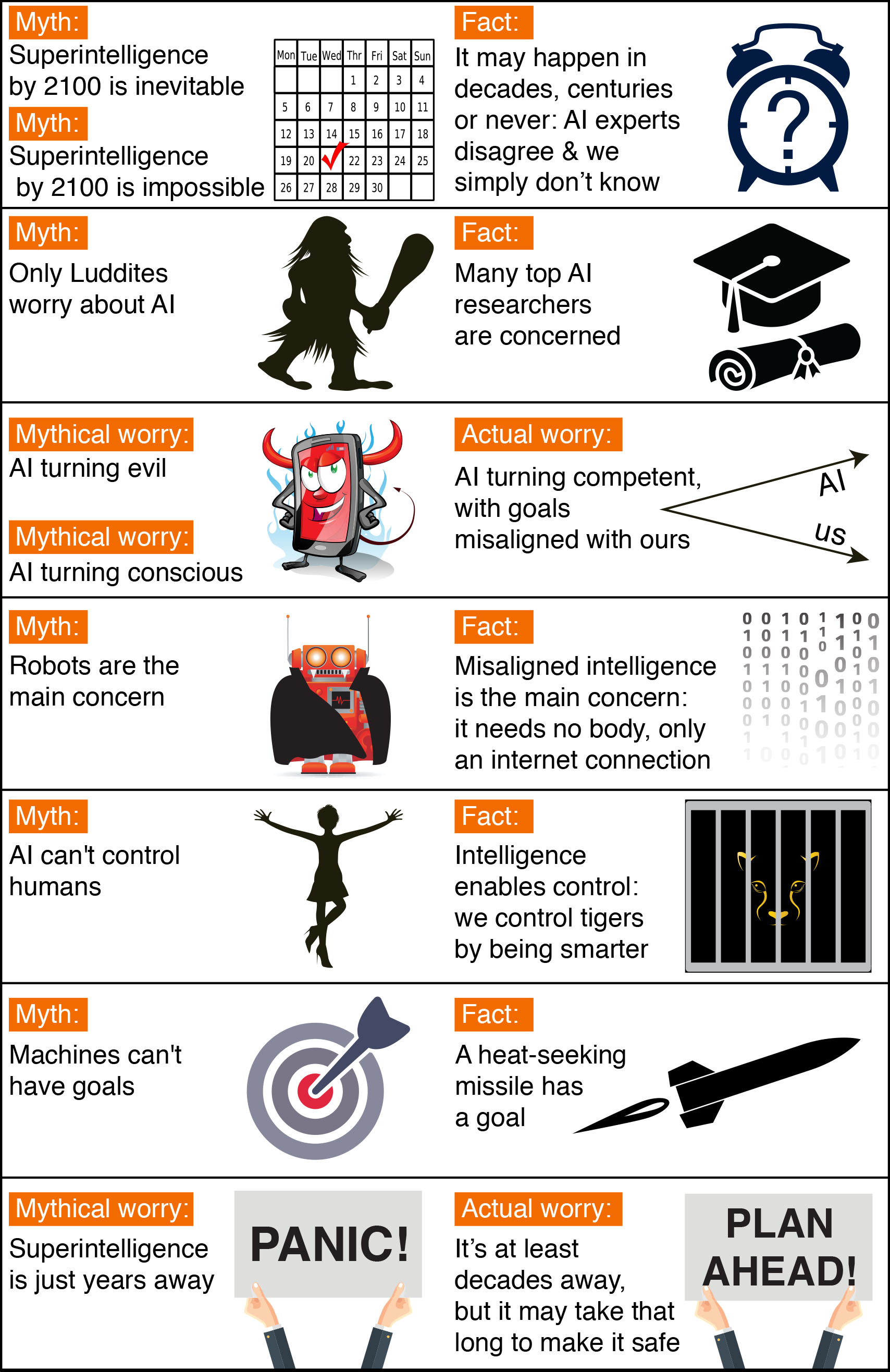
HOW CAN AI BE DANGEROUS?
Most researchers agree that a superintelligent AI is unlikely to exhibit human emotions like love or hate, . When considering how AI might become a risk, experts think two scenarios most likely:
The AI is programmed to do something devastating: Autonomous weapons are artificial intelligence systems that are programmed to kill. In the hands of the wrong person, these weapons could easily cause mass casualties. Moreover, an AI arms race could lead to an AI war that also results in mass casualties. To avoid being misused by the enemy, these weapons would be designed to be extremely difficult to simply “turn off,” so humans could plausibly lose control of such a situation. This risk is one that’s present even with narrow AI, but grows as levels of AI intelligence and autonomy increase.
The AI is programmed to do something beneficial, but it develops a destructive method for achieving its goal: This can happen whenever we fail to fully align the AI’s goals with ours, which is strikingly difficult. If you ask an obedient intelligent car to take you to the airport as fast as possible, it might get you there chased by helicopters and covered in vomit, doing not what you wanted but literally what you asked for. If a superintelligent system is tasked with a ambitious geoengineering project, it might wreak havoc with our ecosystem as a side effect, and view human attempts to stop it as a threat to be met.


nice article :)
ReplyDeleteThanks you Green Warrior for the kind comment! 😄
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteThanks for Sharing a useful information. Its really helpful for us
ReplyDeleteartificial intelligence course
Artificial Intelligence Online Training
AI Certification
Artificial Intelligence Certification
Online Artificial Intelligence Course